How important is adaptation to climate change? Climate change is transforming our lives. It has implications for nature, the economy, and society. Higher temperatures, more hot days, melting glaciers, and more frequent occurrences of flooding and wildfires are just a few examples of visible and measurable changes. It is no longer a question of whether we practice climate protection or adapt to the consequences of climate change, both are vital to survival.
The fact that climate protection must be a part of our lives has long been clear. However, awareness that adapting to the consequences of climate change is also essential has only come into focus in recent years.
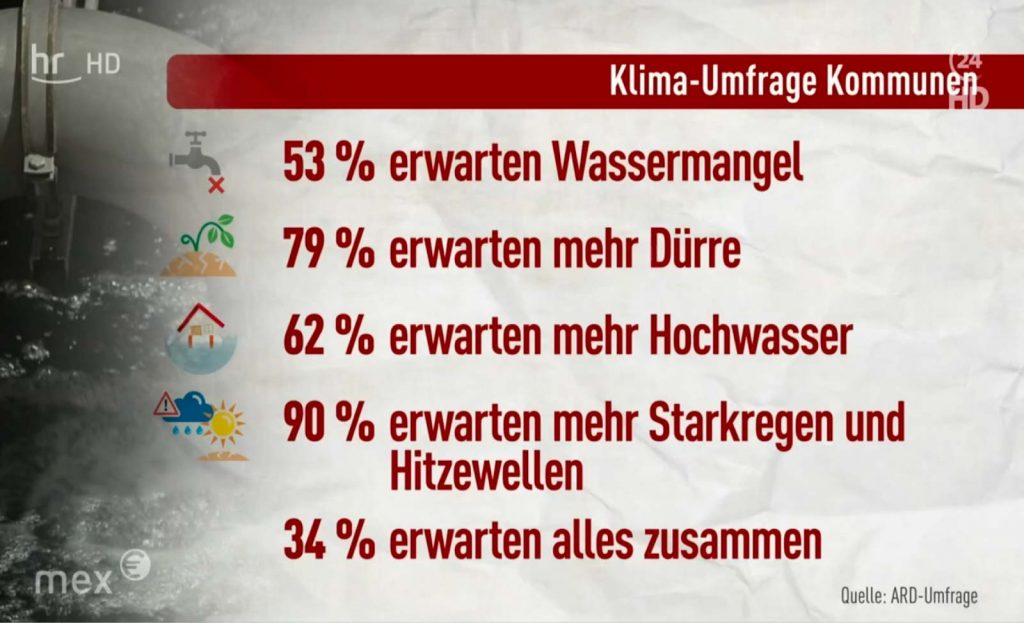
What does climate adaptation mean? The European Commission defines it as:
„Adapting to climate change means taking action to adjust to its present and future impacts.”*
Individual nations derive their strategies from this. In Germany, this is the “Adaptation Strategy to Climate Change,” first developed in 2008. It defines fifteen different areas of action. Based on this, updated action plans are continually being developed. They specify concrete measures that federal government and federal-state cooperation shall implement.**
What are the biggest challenges to climate adaptation? The most significant challenges to our adaptability are the consequences of extreme weather conditions, such as heavy rain, drought, heat waves, storms, and floods. A survey by the German Institute for Urbanistics shows the development of these disasters since 2008:
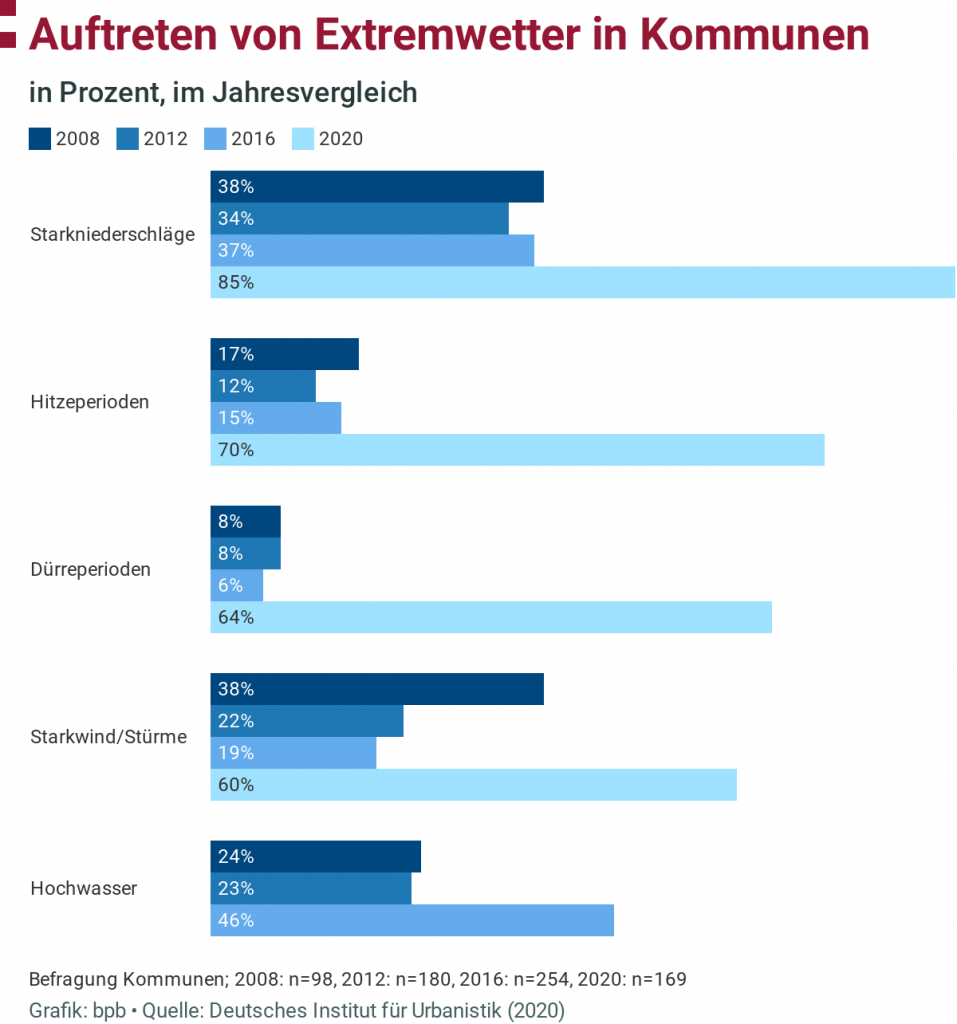
“The natural disaster that claimed the most lives worldwide in 2019 was the heatwave in Europe with 2,500 deaths.”** While the consequences of climate change have long been obvious and life-threatening in the Global South, awareness of the dangers has only slowly awakened in Germany. Catastrophes such as the flood in the Ahr valley and increasingly hot summers are sensitizing more people to the fact that climate change has threatening consequences.
What measures do we take for climate adaptation?
When it comes to specific measures, cities and municipalities are particularly called upon. Examples of municipal climate adaptation measures are heat or heavy rain danger maps. Citizens can recognize which parts of the city are at particularly high risk and need to take precautionary measures. Urban development measures for unsealing and vertical greening are examples of adaptation services. The idea behind so-called sponge cities is to store water and lower temperatures in summer. Another measure to protect the population from heat dangers is the installation of drinking water fountains. The federal government provided the template with the amendment of the Water Resources Act in January 2023. Now the offer of free water is an integral part of basic services.
The installation of drinking water fountains is a good example of how to meaningfully connect climate adaptation and climate protection. The free drinking water helps to reduce the danger of dehydration. Moreover, the fountains offer the possibility to refill brought water bottles repeatedly, thus reducing the consumption of environmentally harmful plastic bottles.
Climate Adaptation with the Klima-Taler App
The Klima-Taler App also connects climate protection and adaptation to climate change. We want to support cities and municipalities with the app to playfully achieve their climate goals. If you walk, cycle, or use public transportation, you earn valuable climate coins for the saved CO2. Along with many features that motivate climate-friendly behavior, we have also compiled tips and measures for heat protection for users. Following these protects you and your fellow human beings from the dangers of high temperatures. For that, too, the users earn climate coins, which they can exchange for rewards. Brand new in the app is the map with drinking water fountains. If you share your location, you can now easily find the nearest drinking water fountain with the Klima-Taler App.
Conclusion Climate Adaptation and Climate Protection:
There are many measures that help adapt to new living conditions and make the consequences of climate change more bearable. But every adaptability has its limits. Today, there are ecosystems that are irretrievably destroyed. Once a certain global warming is reached, some consequences cannot be reversed, such as the thawing of permafrost soils. They release trapped methane hydrate during the thawing process, which in turn accelerates climate change. On the other hand, it’s too late to rely solely on climate protection. Because the consequences of climate change are already devastating today. Therefore, the issues of “climate protection” and “adaptation to climate change” can never be either-or. To achieve as much as possible, we must pursue both strategies with diverse measures, both small and large, consistently and with all our might.
Here you can find more information about the Klima-Taler Aphttps://klima-taler.com/p.
* https://climate.ec.europa.eu/eu-action/adaptation-climate-change_en
** https://ec.europa.eu/commission/presscorner/detail/de/ip_21_663

